- Home
- Prototypes
- CSpace
CSpace
CSpace: a concept embedding space for biomedical applications
The ability to measure similarity and relatedness between bio-medical concepts is crucial to enable downstream applications such as semantic search, gene-disease association, and drug repurposing, among others. Recent research trends rely on transformer-based architectures to learn contextual embeddings directly as a part of the deep-learning pipeline. Unfortunately, this approach i) is not well suited to embed single bio-medical concepts and ii) requires specialized hardware to be trained and even run. To overcome these problems, we built CSpace, a compact concept embedding for the bio-medical domain with minimal computational requirements both at training and inference time.
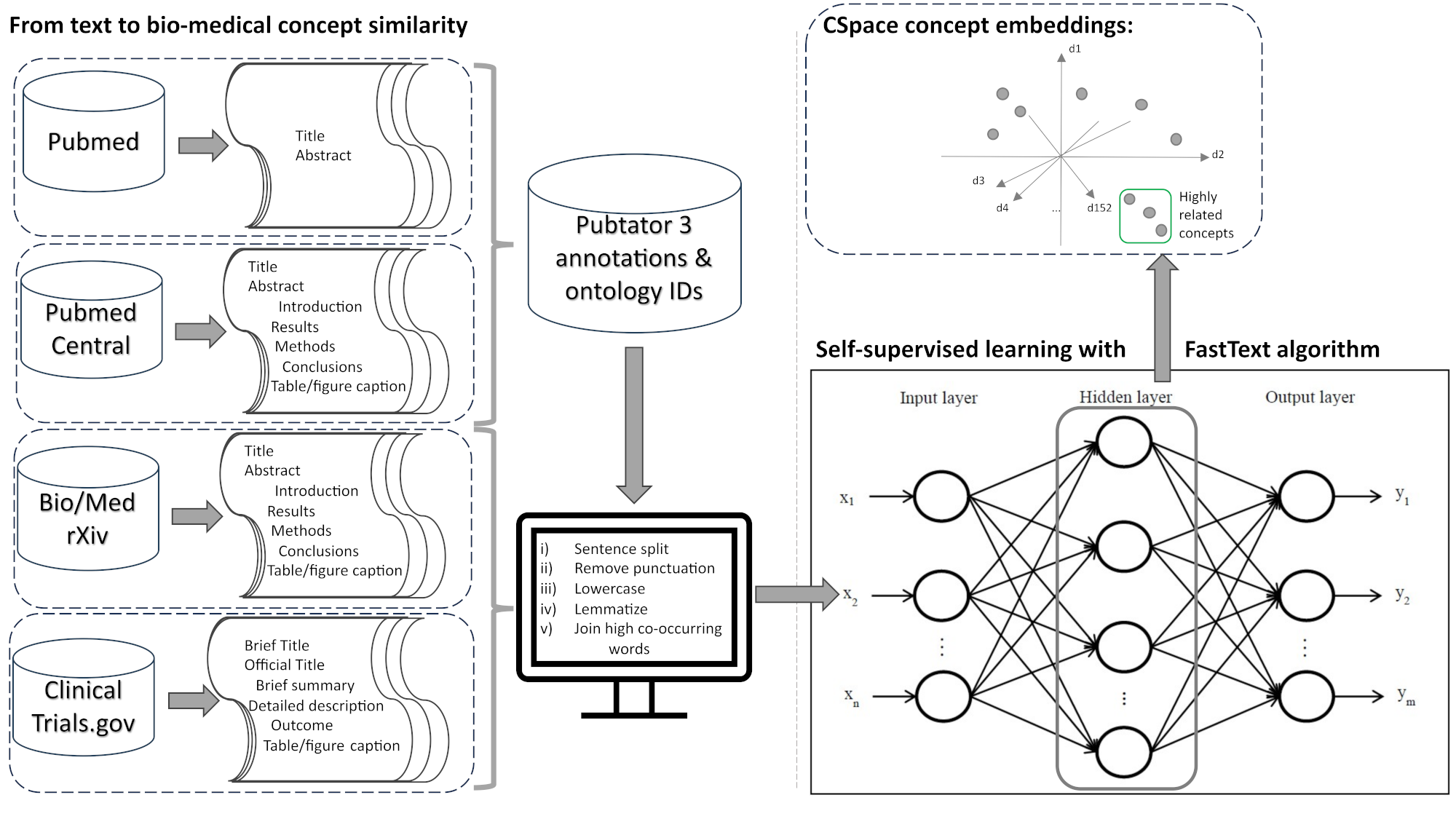
CSpace offers an efficient method for modeling biomedical concepts, ontological identifiers, and short sentences with significantly reduced computational cost compared to transformer‐based models.
Its performance was rigorously evaluated using standard human‐level benchmarks for both concept (Table 5) and sentence (Table 7) similarity. For concept similarity, CSpace was compared to previously published models and OpenAI ada-v2 on UMNSRS (similarity and relatedness) and MayoSRS datasets, demonstrating superior results and providing unique ontological identifier embeddings.
In sentence similarity assessments on the BIOSSES dataset, CSpace consistently outperformed BioWord2Vec and BERT-Crel-all, with a performance penalty below 5% compared to OpenAI ada-v2 while using less than 10% of ada-v2 embedding dimension (152 versus 1536).
Further, CSpace supports cross-ontology concept comparison, providing a method to quantify, for instance, gene-disease association strength based on biomedical literature.
References
Danilo Tomasoni, Luca Marchetti, CSpace: a concept embedding space for biomedical applications, Bioinformatics, July 2025 link